- CARE WELCOME MR. ERIC SOULIER, COUNSELLOR FOR COOPERATION AND CULTURAL AFFAIRS AT THE FRENCH EMBASSY IN VIETNAM AND DIRECTOR OF THE FRENCH INSTITUTE IN VIETNAM
- CARE HOSTS FRENCH PIANIST DANA CIOCARLIE FOR A SAIGON RIVER FIELD TRIP
- NEW PROJECT AT CARE: OCCURRENCE OF EMERGING CONTAMINANTS (CECS) AND DISINFECTION BY-PRODUCTS (DBPS) IN THE DRINKING WATER SUPPLY SYSTEM AND PROPOSAL OF MITIGATION SOLUTIONS FOR HO CHI MINH CITY
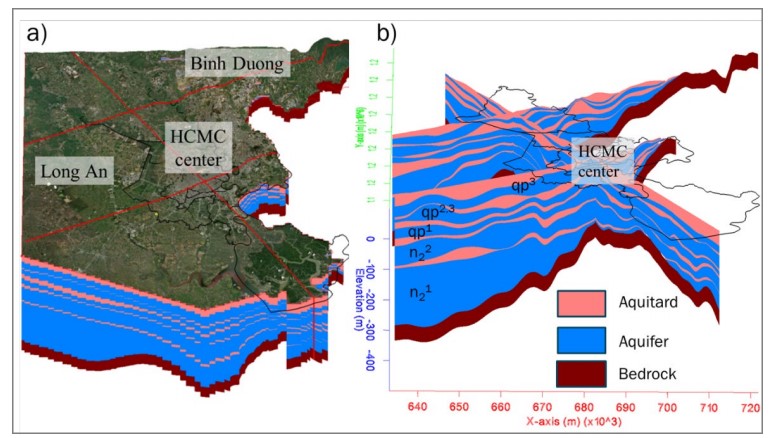
Understanding Impacts of Groundwater Extraction on Flow Dynamics in Multi-aquifers of Ho Chi Minh City Area, Vietnam
13/01/2025 12:05 PM GMT+7 TP HCM
We are pleased to introduce the research article titled "Understanding the Impact of Groundwater Extraction on Flow Dynamics in Multilayered Aquifers in Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam" by authors Quang-Khai Ha and Sucharit Koontanakulvong, published in the Journal of Water Management Modeling (2024).
This study is a key contribution to the project “Enhancing Research Capacity and International Collaboration of the Centre of Asian Research on water” by CARE, and was funded by Vietnam National University Ho Chi Minh City (VNU-HCM) under grant number DA2024-20-01.
Understanding the dynamic characteristics of the groundwater flow budget is crucial for effective water management. This study investigates the groundwater budget in the Ho Chi Minh City (HCMC) area by the application of groundwater flow modeling. A 3D model was built to simulate groundwater flow in aquifer systems in Ho Chi Minh City, using extensive hydrogeological data from 400 borehole logs, along with climate, hydrological, and groundwater extraction data. The model was calibrated in both steady-state and transient conditions, with monthly data from 1995–2007, and then validated using five years of monthly groundwater level monitoring data from 2008–2012. In general, the calibrated and validated models show a good match between calculated and observed groundwater levels,with R2 values > 0.8. The model results illustrate that recharge rates in HCMC vary according to local geological conditions and fluctuate seasonally due to changes in climate factors such as rainfall and evaporation. The annual recharge rate did not significantly change during 1995–2012. A groundwater depression cone was observed in the city center, with a maximum groundwater level approximately 50 meters below mean sea level (bmsl). Groundwater extraction increased sixfold from 1995–2012, which is the main cause of groundwater level decline. This study also found that the river system plays an important role in maintaining the groundwater balance in the area. As a result, increased groundwater exploitation has induced a fourfold rise in river leakage, while groundwater discharge to the river decreased by 35% during the same period. These changes potentially contribute to increased risks to groundwater quality, a reduction in base flow within the river system, and greater vulnerability of the natural ecosystem.
For detailed insights, access the full article here: https://doi.org/10.14796/JWMM.S533
Related news
The Scientific Council meeting of Centre of Water Research in Asia (CARE)
On 22/10/2015, CARE has organized the meeting of the Scientific Council with the chairmanship of Dr. Nicolas Gratiot - Director and Chairman of the Scientific Council, Assoc. Pro. Vo Le Phu (on behalf of Assoc. Pro. Nguyen Phuoc Dan - Deputy Chairman)
22/10/2015
USTH_2016: Call for PhD. Candidate 2016 in remote sensing.
Project description The availability of High Resolution Imagery (spatial, spectral, and radiometric) with an increased time revisit (Landsat-8 and now Sentinel-2) opens the way to a more detailed observation of coastal zones and inland waters (large rivers, lakes and reservoirs)
26/02/2016
RD DELEGATION VISIT CARE-RESCIF
On 08 September 2016, the delegation from Institute of Research for Development (IRD – France) led by Mr. Thierry Lebel - Director of the Promotion of Interdisciplinary and Intersectoriality and Mr. Frédéric Ménard
02/09/2016
UNESCO Monography: HCMC growing with water-related challenges
The pretty work, a monography collection of 15 megacities in the world about "Water, megacities and Global Change”, has been published by UNESCO. The CARE Lab-HCMUT Researchers are honored to represent Ho Chi Minh City by contributing an article
11/10/2016
Fulltext of the Monography "Ho Chi Minh City growing with water-related challenges" available
CARE Lab-HCMUT is pleased to present you our publication of the monography "Ho Chi Minh City growing with water-related challenges".
31/10/2016
CARE Lab-HCMUT at the environmental technology exhibition POLLUTEC, Lyon
CARE Lab-HCMUT and PADDI, a member of the Ho Chi Minh City delegation, participated in the 26th Environment exhibition POLLUTEC, Lyon (France), which took place from 30/11 to 02/12/2016.
22/12/2016
SUJETS DE STAGE AU CARE-Rescif 2017
Tuteur: Dr. BUI Xuan ThanhAssociate Professor in Environmental Engineering,Head, Department of Water Science & Technology Faculty of Environment & Natural Resources
11/01/2017


666